Materiality for the Ricoh Group
Ricoh Group’s Management Strategies and Identification of Material Issues
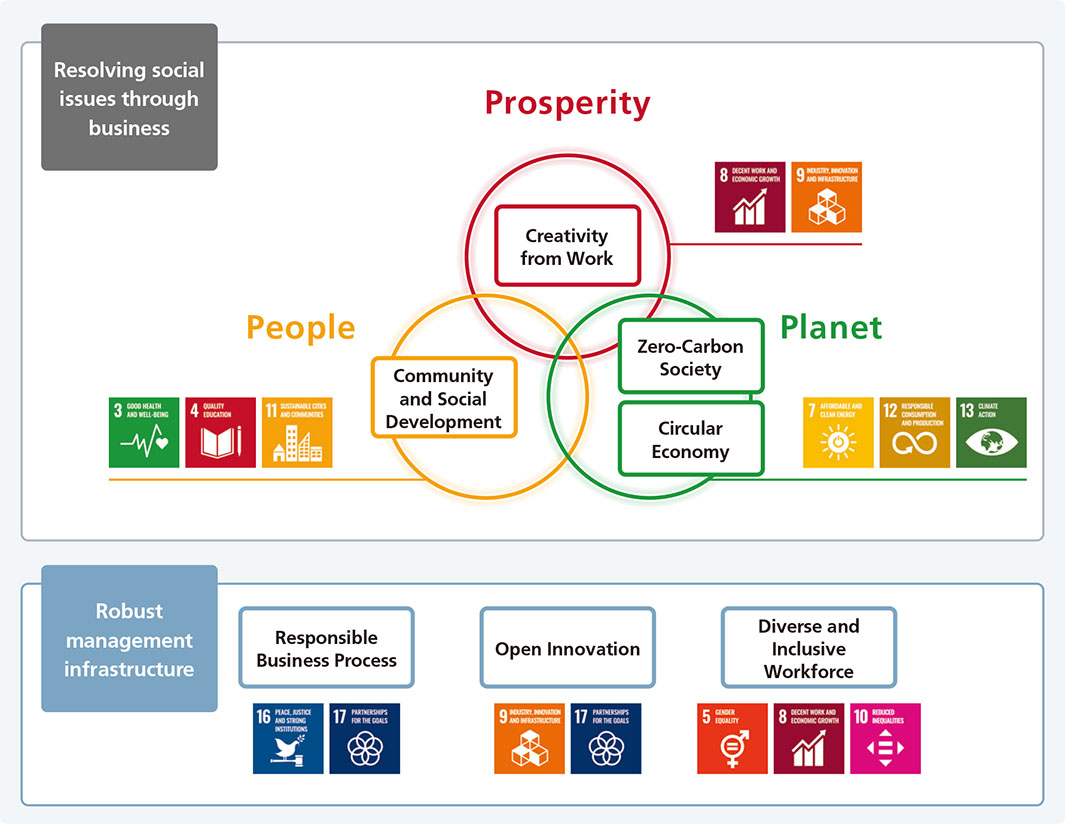
For the Ricoh Group, an ideal sustainable society is one in which the Three Ps Balance—balance between Prosperity, People and Planet is maintained. In order to create such a society, we will work to solve social issues through business based on the material issues identified by reflecting Ricoh’s Mission Statement, Mid-Term Management Strategy and expectations of our stakeholders, which are reviewed and set in conjunction with the formulation of our Mid-Term Management Strategy every three years.
Seven Material Issues and SDGs
| [Materiality] | [Strategic Intent] | |
|---|---|---|
| Resolving social issues through business | Creativity from Work | To provide digital services that transform how customers work, and help them with productivity improvement and value creation |
| Community and Social Development | To contribute to the maintenance, development, and efficiency of community and social systems. We leverage our technical expertise and customer connections to expand the areas where we provide value. | |
| Zero-Carbon Society | To decarbonize the entire value chain and create business opportunities by contributing to carbon neutrality | |
| Circular Economy | To create business opportunities by building a circular economy business model for ourselves and our customers |
| [Materiality] | [Strategic Intent] | |
|---|---|---|
| Robust management infrastructure | Responsible Business Process | To earn stakeholder trust by taking a holistic view of our supply chain and minimizing ESG risks in our business processes |
| Open Innovation | To shift from a self-sufficient approach to a new value creation process that creates business to quickly resolve social issues | |
| Diverse and Inclusive Workforce | To foster a corporate culture where diverse employees can demonstrate their potential and transform themselves and the company into one that is resilient to change |
<16 company-wide ESG targets and achievements linked to seven material issues>
Resolving social issues through business
| Materiality (Material issues) |
2030 targets | Focus Domains | ESG targets in 21st Mid-Term Management Strategy (End of FY 2025) |
FY2023 achievements | FY2024 achievements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Creativity from Work |
Contribute to “Creativity from Work” for all customers to whom we deliver value |
|
(i) Customer survey scores*1 | 29% |
|
|
|
Community and Social Development |
Contribute to the enhancement of social infrastructure for 30 million people |
|
(ii) Number of people to whom we have contributed by improving social infrastructure | 23.5 million people | 17.94 million people | 22.35 million people |
|
Zero-carbon Society |
Reduce GHG*4 emissions by 63% for scope 1 and 2, and 40% for scope 3 Switch to 50% renewable electricity |
|
(iii) GHG scope 1, 2 reduction rate (vs. 2015) | 50% | 47.4%*5 | 59.1% |
| (iv) GHG scope 3 reduction rate (vs. 2015) | 35% | 38.1%*5 | 46.8% | |||
| (v) Renewable energy usage ratio | 40% | 31.0%*5 | 43.2% | |||
| (vi) Avoided emissions |
1,400 thousand tons |
1,059 thousand tons |
1,448 thousand tons |
|||
|
Circular Economy |
Use resources efficiently across the value chain and reduce the virgin material consumption rate to 60% or less | (vii) Virgin material usage rate | 80% or less | 78.9% | 78.3% | |
-
*1The percentage of customers who evaluated us as a digital services company
-
*2A survey targeting solution customers in LA
-
*3APAC: Asia Pacific
-
*4GHG: Greenhouse Gas
-
*5Due to changes in organizational structure, the scope of disclosure has been revised and related figures have been recalculated.
Robust management infrastructure
| Materiality (Material issues) |
ESG targets in 21st Mid-Term Management Strategy (End of FY 2025) |
FY2023 achievements |
FY2024 achievements |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Responsible Business Process |
(viii) CHRB score*6 | ICT sector leader | Self-assessment completed. 55% progress toward target | Self-assessment re-performed. 90% progress toward target |
| (ix) Compliance with NIST SP800 -171 Coverage of Ricoh’ s core business environment | 80% or more | Continued identification and assessment of information to be protected | Identification of information to be protected and formulation of a plan completed. Countermeasures partially completed. | |
| (x) Low-compliance risk group companies | 80% or more | Completed pulse survey for high-risk organizations | Improvement measures developed in the high-risk organization. Implementation partially completed. |
|
|
Open Innovation |
(xi) Contracted Joint R&D ratio | 25% | 23.0% | 22.7% |
| (xii) Digital service patent application ratio*7 | 60% | 54.7% | 64.6% | |
|
Diverse and Inclusive Workforce |
(xiii) Ricoh Digital Skills Level 2 or above rated employees (Japan) | 4,000 people | 2,855 people | 4,658 people |
| (xiv) Process DX Silver Stage-certified employee ratio*8 | 40% | 21.1% | 34.2% | |
| (xv) Engagement score *9 |
|
|
|
|
| (xvi) Female-held managerial position ratio |
Global:20% Japan:10% |
Global:16.5% Japan:7.7% |
Global:17.2% Japan:8.4% |
|
-
*6CHRB (Corporate Human Rights Benchmark) Score: An international human rights initiative established by institutional investors and NGOs. It evaluates global companies from five sectors: food and agricultural products, apparel, extractives, ICT manufacturing, and automotive manufacturing. (Approximately 250 companies evaluated as the latest benchmark)
-
*7Ratio of patent applications related to digital services business to total patent applications
-
*8Training rate of personnel with process improvement experience based on a Process DX model (Denominator is the total number of personnel in the training target organization of each business unit.)
-
*9Uses Gallup’s Q12 mean score (evaluation scores for 12 factors to predict high organizational performance)
Materiality Analysis
Materiality-specific process

STEP 1: Identifying Issues
In considering our mid-term management strategy, we assess the risks and business opportunities arising from changes in environmental and social trends—such as increasing demands to address climate change and human rights. At the same time, we evaluate the impact of our business activities on the environment and society, and identify key issues that require action.
STEP 2: Prioritizing Issues
Prioritize the identified issues based on international guidelines such as the SDG Compass, GRI standards, and the concept of double materiality, as well as management philosophy, management and business strategies, opinions from external stakeholders, and priority management risks in line with the risk management system. The drafts of materiality and ESG targets are then prepared.
Step 3: Management Decision
The materiality and ESG goals are deliberated and decided upon by the ESG Committee, which consists of the CEO as the Chairman, all Internal Directors, and Executive Officers. These decisions are made in conjunction with the financial goals of the mid-term management strategy and are approved by the Board of Directors before disclosure.
STEP 4: Performance Disclosure
Annual performance against ESG targets is disclosed annually by the ESG Committee, after confirmation with management.
Stakeholder opinions referenced
Individual meetings with shareholders/investors/analysts
Feedback from large IR meetings
ESG requests from customers during negotiations
Request in ESG evaluation systems
Opinions from internal stakeholders
Dialogues with external organizations such as JCLP and JCI
Reference Guidelines
SDGs Compass
GRI standard
European Guidelines on non-financial Reporting directive
Ministry of the Environment's Environmental Reporting Guidelines
TCFD
Ten Principles of the United Nations Global Compact
ISO26000
Relationship between executive compensation and ESG indicators
To clarify management's responsibility for ESG initiatives and achieving targets, we have incorporated ESG indicators into executive compensation since the fiscal year 2020.
Relationship to Executive Bonuses
By incorporating the "DJSI* Annual Ratings," which are used as a tool to monitor ESG initiatives, into the performance-based bonus calculation formula for directors and executive officers, we provide incentives for ESG initiatives. Furthermore, executive officers' compensation is also linked to ESG goals within their areas of responsibility, enhancing commitment to achieving ESG targets in each business unit and group headquarters.
* The Dow Jones Sustainability Index (DJSI) is a share index jointly developed by Dow Jones in the US and S&P Global, a company specializing in research on sustainable investment, to measure the sustainability of major companies around the world from the three perspectives of economy, environment, and society.
Relationship to Executive Stock Compensation
Starting from the fiscal year 2023, in addition to bonuses, we have introduced performance-based stock compensation with ESG targets for directors. The number of ESG targets achieved by the company is linked to the payment rate. Furthermore, this system will also be introduced for executive officers from the fiscal year 2024.
Approach to Materiality (Material issues)
The Ricoh Group's policy is to “Align ESG with business growth.” We position ESG initiatives as future financial targets because we look for them to bear financial fruit three to five years hence. We identify four material issues for “Resolving social issues through Business”, and we regard them as particularly significant business opportunities. By leveraging our strengths in these areas, we aim to drive further business growth. We would like to introduce our activities.

