- Home
- Sustainability
- Environment
- Environmental Information of Our Products
- Resource Conservation / Recycling - Reduction of water consumption
Products:Resource Conservation / Recycling
-Reduction of water consumption-
Reducing water consumption more than 90% with RECO-View RF Tag Sheets
The RECO-View RF Tag Sheet is a medium developed by combining Ricoh’s rewritable technology and automatic recognition technology for RF tags. Replacing conventional hard copies (paper sheets) with RF Tag Sheets in product management and process control will improve work efficiency while reducing costs and paper consumption*1 at production sites. We evaluated the influence of the reduction of paper consumption attributable to the medium on water resources by calculating the Water Footprint (WFP).
The result indicated that use of RF Tag sheets can cut the amount of water consumption radically by more than 90% throughout the lifecycle of paper. This reflects the fact that the largest amount of water is consumed during the raw material stage.
*1.More information on the reduction of paper consumption is available at here.
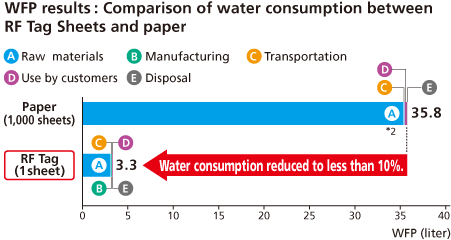
Under the assumption that one RF Tag sheet is rewritten 1,000 times, water consumption was compared between one RF Tag sheet and 1,000 sheets of paper with regard to their lifecycle, including procurement of materials and parts, product manufacturing, use of products by customers, and collection and disposal of used products.
Note: Calculations were conducted at the WFP Jissen-juku (WFP implementation school) with the support of Prof. Norihiro Itsubo of Tokyo City University, who also verified the data.
*2.To allow the use of inventory data for paper (1,000 sheets), water consumed during the paper manufacturing process is included when determining the amount of consumption used by materials.
What is a Water Footprint?
– A yardstick to measure the water consumption of products over their lifecycle –
Of the 1,386,000,000 cubic kilometers (km3) of water that exists on the Earth, only 2.5% comprises fresh water used to sustain human life. While Japan has relatively abundant water resources, people in many countries in the world do not have access to hygienically safe water in their daily lives. The issue of water resources shortage is thus a serious challenge.
In addition to using drinking water in our daily lives, we use water at every stage in the lifecycle of products, including foodstuffs, clothes, paper and home appliances. Thus, we must have a "yardstick" to measure the amount of water consumed with regard to the goods and services we use. One such yardstick is the Water Footprint, which allows us to determine how much water is consumed at each stage of the product lifecycle (from material procurement to product disposal). The results are used to formulate plans for water consumption reduction (reducing water consumption by changing manufacturing processes or water usage, for example) and to verify the effects of the plans.