- Home
- About Ricoh
- Company History
- Starting out — entering the business machine field
Company History
Starting out — entering the business machine field
Ricoh’s origins date to a decision of the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research to commercialize the fruits of its R&D by setting up Rikagaku Kogyo. In 1936, Rikagaku Kogyo established Riken Kankoshi Co., Ltd. (renamed Riken Optical Co., Ltd., in 1938, and Ricoh Company, Ltd., in 1963), to manufacture and sell sensitized paper. The Company started its camera business in 1937. In 1950, it created Japan’s first mass production structure for cameras, driving their popularity among consumers. The company entered the business machine field in 1955 by launching the Ricopy 101.
- Feb. 6, 1936
-
The sensitized paper division of Rikagaku Kogyo split off to be established as Riken Kankoshi Co., Ltd. (–1938)
Learn more
The sensitized paper division of Rikagaku Kogyo split off to be established as Riken Kankoshi Co., Ltd. (–1938)

- Kiyoshi Ichimura

- Institute of Physical and Chemical Research in the earliest days (Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo)

- Head office of Riken Optical Industries, Ltd. renamed from Riken Kankoshi Co., Ltd. (Ginza 8-chome, Tokyo; 1938)
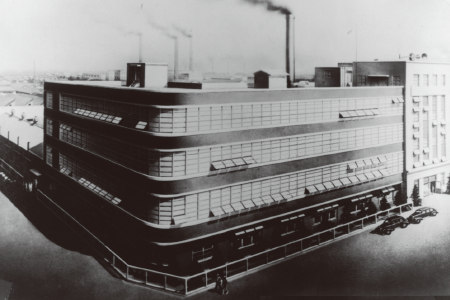
- Oji Plant, the main factory of Riken Optical Industries for manufacturing sensitized paper as well as cameras and binoculars (1938)
Founder Kiyoshi Ichimura
Ricoh’s origins date back to a decision by the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research to commercialize the fruits of its R&D by setting up Rikagaku Kogyo. Since its formation in 1927, the business venture has placed on the market numerous products developed by the research institute, including sensitized paper. On February 6, 1936, the sensitized paper division was split off to be established as Riken Kankoshi Co., Ltd., a precursor of Ricoh, under the directorship of Kiyoshi Ichimura (1900-1968). As the founder of Ricoh, Ichimura led the successful development of the business that started with 350,000 yen in capital and a staff of 33.
Kiyoshi Ichimura formulated The Spirit of Three Loves: “ Love your neighbor,” “ Love your country,” “Love your work,” and ever since, they have been respected as the Ricoh Group’s Founding Principles, which provide every employee with a guide for business and encourage individuals to constantly improve and contribute to the wellbeing of all stakeholders, including families, customers, and society at large.
The Birth of RICOH
- Mar. 1938
-
Riken Kankoshi Co., Ltd. renamed Riken Optical Co., Ltd. and starts production of optical devices and equipment.(until 1963)
- Jan.12, 1946
-
Kiyoshi Ichimura appointed president (until Dec.16, 1968)
- Mar. 1950
-
Launches the Ricohflex III camera, which spurred the popularization of cameras.
Learn more
Launches the 6x6 format TLR Ricohflex Model III, which spurred the popularization of cameras in Japan

- Ricohflex Model III (1950)

- In 1953, Ricoh became Japan's first manufacturer to introduce a belt-conveyor production system. For its successful establishment of the mass production system, Ricoh was recognized by the Okochi Memorial Foundation with a production award.

- Ricoh was awarded the Okochi Memorial Production Prize for the successful establishment of a mass production system (1957)
Ricoh was the first company in Japan to introduce a belt-conveyor system for manufacturing cameras, achieving a production capacity of 10,000 units/month—more than ten times the capacity of the then standard level of less than 1,000 units/month from the conventional handicraft industry. Successfully adopting this method of camera mass production, Ricoh offered the Ricohflex Model III at an affordable price, which was remarkably low for an iconic luxury item in those days. This model became highly popular among Japanese consumers, reportedly representing more than 50% of total national camera production during its sales peak.
- Apr. 1953
-
Ohmori Plant opens in Ota-ku, Tokyo, through merger of affiliate companies Asahi Seimitsu Kogyo Co., Ltd. and Aiko Trading Co., Ltd.; camera manufacturing resumed.
- Nov. 1955
-
Introduced Ricoh's first diazo copier, “Ricopy 101.“
Learn more
Introduced Ricoh’s first diazo copier, Ricopy 101
—Included in the Mechanical Engineering Heritage list

- The oldest existing Ricopy 101 model

- Production line of Ricopy 303 and 505 models (1957)

- Advertisement for Ricopy
In 1955, Ricoh launched its first office copier, the Ricopy 101. The product became widely popular in the late 1950s, sparking the coining of the term “make a Ricopy,” meaning to “make a copy” in Japan, a representation of the brand that came to be recognized as being synonymous with the concept of duplication. Ricopy 101 and the following desktop diazo-wet copier Ricopy series brought about a revolutionary improvement in office work efficiency, ushering in an age of office automation. The model received the Mechanical Engineering Heritage Certification No.54 for fiscal year 2012.
Related website:Ricopy 101: Forerunner of Office Automation
- Jan. 1957
-
Establishes Japan's first mass-production system for cameras. Awarded Ohkochi Memorial Production Prize for techniques to mass-produce cameras.
- Jul. 1960
-
Sindo Koeki Co., Ltd., a joint venture, founded in Korea (renamed Sindo Ricoh Co., Ltd. in 1970).
- Aug. 1960
-
Introduces the “RICOH OFFSET“ duplicator, leading to low-cost high-volume copying in the office.
- May 1961
-
Osaka Plant opens in Ikeda, Japan to manufacture sensitized paper.
- Apr. 1962
-
Numazu Plant, Japan, formed. It features the world's first fully integrated production system of sensitized paper.
Learn more
The Numazu Plant’s functions enhanced to establish an integrated production system for sensitized paper

- Current Numazu Plant (South Plant)

- Electrofax paper coating line (Numazu Plant)
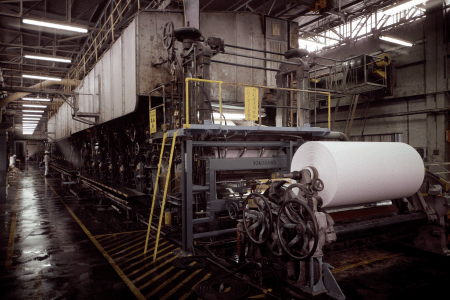
- Paper machine in Numazu Plant, completed in March, 1960
A paper factory was completed in April 1960 in Numazu, Shizuoka Prefecture. Two years later, the plant was expanded by building facilities for manufacturing sensitized paper on the same premises, thereby establishing an integrated production system for sensitized paper that included the base paper manufacturing process—the first of its kind in the world.
- May. 1962
-
Ohmori Plant and General Research Laboratory completed.
Learn more
Ohmori Plant and General Research Laboratory completed

- Completion of the Ohmori Plant (for manufacturing office machines) and the General Research Laboratory

- Prime Minister Hayato Ikeda at the opening reception with Ricoh president Kiyoshi Ichimura in May 17, 1962
In May 1962, the Ohmori Plant (for manufacturing offce machines) and General Research Laboratory were completed on the premises where the head offce was located. They served as strong Ricoh bases to support expansion of its business areas of microphotography cameras, offset printers, data processing systems, and many others.
- Nov. 1962
-
Introduces the “Ricoh Auto Half“, a half frame camera that proves to be a massive hit
Learn more
Introduces the Ricoh Auto Half, a half frame camera that proves to be a massive hit

- Ricoh Auto Half (1963)

- Size comparison to a tobacco box
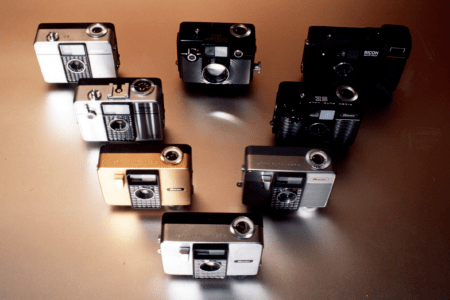
- Auto Half series
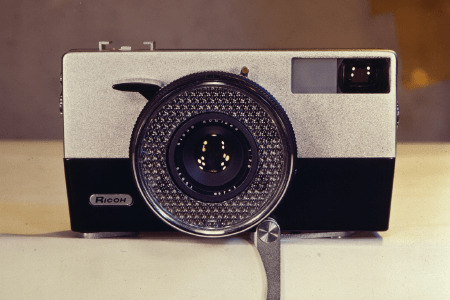
- Ricoh Auto 35
Ricoh is a leading pioneer in the field of automatic camera technologies. In 1960 it released Ricoh Auto 35, the first electric-eye camera developed by a Japanese company; and then in 1962, rolled out the more advanced and handy Ricoh Auto Half—a half-frame, fully automatic camera with automated exposure, focusing and film-winding functions. Being compact, purse-sized and requiring no manual control skills, the world’s smallest popular-model automatic camera of the times proved to be a huge hit, particularly with female consumers.
- Dec. 1962
-
Founded Ricoh Industries, U.S.A., Inc.
- Apr. 1963
-
Changes corporate name to Ricoh Company, Ltd.
Learn more
Changes corporate name to Ricoh Company, Ltd.

- Advertisement announcing the change of corporate name (1963)

- Introduction of Ricoh’s corporate logo in 1963
Since being renamed Riken Optical Co., Ltd. in 1938 to represent its diversified business more accurately, the corporate name remained unchanged for a quarter century until April 1963 when the present name, Ricoh Company, Ltd., was adopted in recognition of the company reaching the key milestone of 10 billion yen in sales in the early 1960s. The company made a fresh start under the new name, aiming to make further quantum leaps.
- Apr. 1963
-
Ricoh (Europe) S.A. established in Switzerland.(running until 1971)
- Mar. 1965
-
Taiwan Ricoh Co., Ltd. founded in Taiwan.
- Sep. 1965
-
Introduces the “Ricopy BS-1“ as its first electrostatic copier
Learn more
Introduces the Ricopy BS-1 as its first electrostatic copier

- Ricopy BS-1 (1965)

- Ricopy BS-1 installed on the Fuji Antarctic researchship (1966)

- Campaign advertisement for Ricopy (1965)
Ricopy BS-1 was introduced in 1965, and turned out to be a key revenue earner that supported the company in its recovery from slumping business. Employing a fixed-platen structure, which marked the world’s first desktop copier to adopt that assembly, the product featured increased availability in terms of type of subject to be copied, covering not only paper sheets but also almost everything from books, textiles, jewelry, and machine parts to kitchen utensils. Ricopy BS-1 was viewed as a forerunner in an age when technological progress enabled the “duplication of anything you like,” while serving as a driving force for Ricoh’s global business development.
- Jul. 1967
-
Tohoku Ricoh Co., Ltd. established in Miyagi Prefecture, Japan.
- Oct. 1967
-
Sohka Ricoh Co., Ltd. founded in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. (renamed Ricoh Tokki Co., Ltd. in 1972, and then Ricoh Unitechno Co., Ltd. in 1990).
- Dec. 1968
-
Founder and President Kiyoshi Ichimura passes away (16th).

- Jan. 30, 1969
-
Mikio Tatebayashi appointed president (until Oct. 22, 1976).










