
- Home
- Information Security
- Information security at the Ricoh Group
- Providing value
Providing value

The Ricoh Group obtained unified ISMS (Information Security Management System) certification in 2004, and we have repeatedly undergone ongoing audits and renewal audits to date.
During this time, we have responded to the expectations and demands of our stakeholders and have reviewed the scope of application to create trust.
ISMS certification is the result of applying and integrating the ISMS model into our business operations and enhancing its quality.
As the next step, the Ricoh Group is working to optimize the ISMS.
This section gives an overview of the Ricoh Group’s efforts to optimize our ISMS.
Overview of Group efforts to optimize our ISMS
Objective of ISMS optimization
The objective of ISMS optimization is to “integrate ISMS and business operations in order to form an optimal management system that maintains the level of information security.” This is nothing new; it is the very objective of introducing ISMS.
However, if the level of information security drops and incidents and accidents occur, the objective will not be achieved. Moreover, bloated costs due to activities that have lost substance and excessive measures must also be taken into consideration.
Although information security has focused on confidentiality, such as preventing incidents and accidents of personal information leaks, expectations and demands are increasing for information integrity and availability, such as business continuity planning.
<Column> Why is an ISMS used?
ISMS tends to be thought of as having many restrictions and prohibitions on various confidentiality issues, but that is not all.
Information is originally intended to be used for business purposes.
The basic concept of an ISMS is “to maintain and improve the balance of confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets that an organization should protect.”
More simply put, it identifies the information that is important for business purposes and the person who is responsible for managing that information.
(1) Restrict information from those who should not use it (confidentiality)
(2) Maintain information in a correct state at all times (integrity)
(3) Ensure that people who need the information can always access it when they want to use it (availability)
If there is any risk of compromising the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information, the risk assessment database is used to reference with the Ricoh Family Group Information Security Measures (RFG ISMeasures). Then, measures to eliminate or reduce the risk, in other words, a “risk response plan,” are implemented.
This is not for the sake of the ISMS, but for the sake of day-to-day operations themselves. The ISMS is not an objective, but rather a means to an end for business.
The Ricoh Group’s objective is of “information security-based management” where an effort is made to create profit striking a balance between information use and information protection by using information in a secure manner while preventing information from being leaked to unintended parties.
Excerpt from monthly ISMS self-check by Ricoh IT/S Headquarters
Objective of ISMS optimization
To achieve this objective, the following goals must be set and completed
1. Identify the information security level
In order to maintain the level of information security, it is important to identify whether that level is high or low. This is an indication of management’s concern that “we have incurred costs to obtain ISMS certification, but what is the level of information security, and will incidents and accidents really not occur?” By identifying the level of information security, the organization’s strengths and weaknesses can be clarified to spiral up.
2. Transition to audits of effectiveness based on conformity of internal audits
Conformity with standards, regulations, and rules is fundamental. Taking this one step further, internal audits determine whether or not the management system is effective. By shifting the internal audit to a perspective of the effectiveness of the management system, the PDCA cycle is prompted to discover new risks and respond to them.
3. Optimize costs
Much of the cost of ISMS involves “human activities,” including policies, target management, activity plans, risk assessment, and internal audits for each organization.
We will promote optimization of costs by reviewing excessive measures, information security activities that have lost substance, and duplicated tasks in each organization.
Specific initiatives
This describes specific initiatives to realize these goals.
We have defined the organizations to be optimized and attempted to optimize the following items from mechanisms such as ISMS activities (policies, targets, activity plans), risk assessment, education, internal audits, incident reporting, and management review mechanisms.
1. Making common ISMS policies, targets, and activity plans, ISMS documents, risk assessment policies
The information security management organization provides the policies, goals, and activity plans that serve as the ISMS framework. Each organization uses this as is or with modifications, taking into account the characteristics of its functions.
The information security management organization provides common documentation related to ISMS. No ISMS documentation is required at individual organizations.
The information security management organization also makes risk assessment policies common. Information assets to be risk-assessed and risk response through assessment are optimized.
2. Internal audits by the information security management organization
Internal audits are conducted by qualified internal auditors of the information security management organization. In the first year of ISMS optimization initiatives, internal audits were conducted by the management organization for all departments of the organizations to be optimized. In the first year, internal audits were conducted by the management organization on a total of 275 departments (35 organizations in Japan and 4 overseas).
From the following year, internal audits were conducted by sampling based on the established criteria for selecting organizations to be audited.
This is a key part of cost optimization while maintaining information security levels.
Features of internal audits by the information security management organization
Internal audits by the information security management organization have the following features and benefits.
Auditors of the information security management organization conduct uniform audits.
Audits are performed with standardized audit procedures, check sheets, and audit methods, so variations in audit standards and results are minimal.
Audits are conducted on the effectiveness of the management system.
We audit whether the PDCA cycle of the management system is soundly implemented and its effectiveness is confirmed.
Identifying the information security level of the audited organization
The information security level is expressed for example as “B+ (formal),” “A- (adequate),” and it is illustrated in a radar chart for reference.
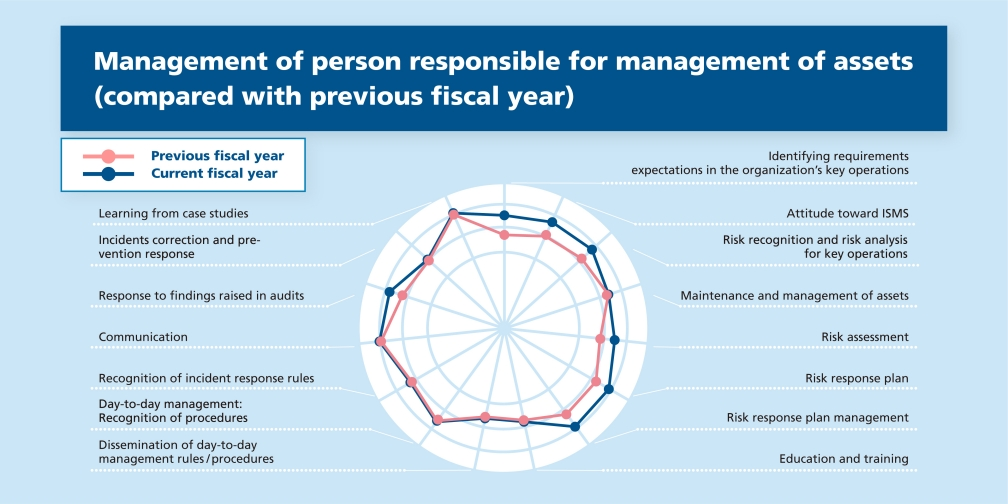 Fig. 1-1 Identifying management level
Fig. 1-1 Identifying management level
Sampling of the audited organization
We sample departments of audited organizations based on factors such as the presence or absence of critical information assets, incidents and accidents, effectiveness of management systems, and information security levels in the previous year.
Effective measures being taken by organizations are recognized as being strong points, and those are introduced at internal audits of other organizations. In addition to strong points, we also provide advice on corrective actions for nonconformities, preventive actions for incidents, and measures to prevent recurrence.
Even after the internal audit is over, we handle consultation on information security and requests for second-party audits, enabling us to build a stronger relationship with the audited organization.